Advanced Mechanical Recycling
The future of plastic recycling
Plastic waste is collected and recovered from any post-consumer waste stream, including residual mixed waste. The recovered plastic is processed with extensive pre-sorting and purification steps to ensure high-quality results.
Advanced mechanical recycling includes:
- Decontamination and label removal
- Flake sorting into polymer types and color groups
- Deodorization
- Extrusion and pelletizing
How does advanced mechanical recycling work?
Advanced mechanical recycling is a revolutionary new technique that transforms household plastic waste into high-quality recycled plastic content.
Advanced mechanical recycling is an energy-efficient method of plastic recycling. Unlike chemical recycling or plastic pyrolysis, it requires far less energy and has a smaller ecological footprint.
At a glance
Advanced mechanical recycling
Discover how advanced mechanical recycling enables the transformation of post-consumer plastic from different material streams into high-quality recycled content.
White paper
Advanced mechanical recycling: Enabling true circularity for plastics, now
Download TOMRA’s new white paper that explores the advanced mechanical recycling process that enables the transformation of post-consumer plastic from different material streams into high-quality recycled plastic content.

Advanced Mechanical Recycling (AMR) has been used to achieve closed-loop (bottle-to-bottle) recycling for PET beverage containers. Today, the AMR process has been upgraded to help achieve circularity for plastic beyond PET beverage containers.
With these upgrades, it is now possible to create virgin-like recycled plastic pellets from source-separated waste streams and mixed waste streams – ensuring that the highest quality recyclate is available to those industries that depend on superior feedstock quality to reduce their C02 emissions and reach recycling and recycled content targets.
TOMRA Talks Circular
Listen to industry experts on our podcast, which aims to affect real change with real conversations.

Laszlo Szekely
Living in a plastic world

Mateusz Wielopolski
Circularity starts with intelligent product design
The plastic supply and demand challenge
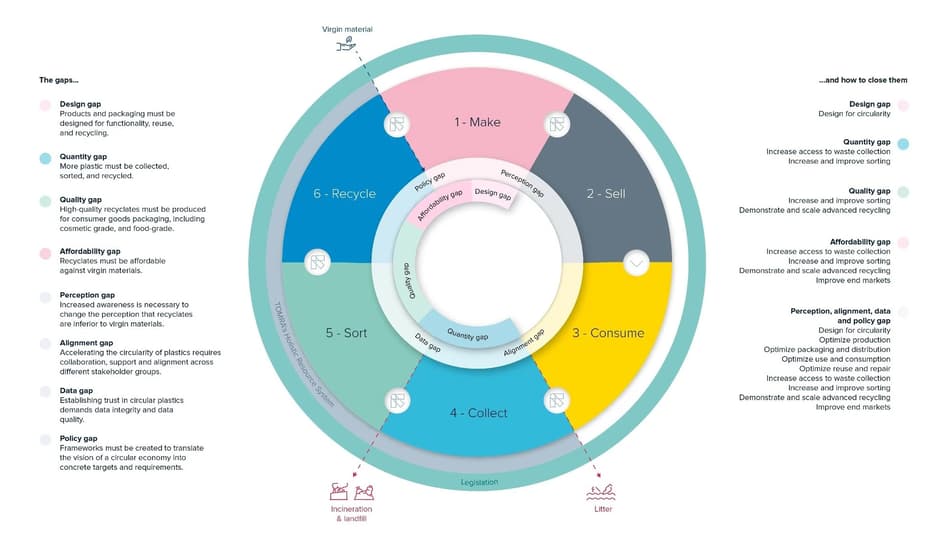
The need to drastically expand the amount of plastic that is recovered is increasing as consumer demand grows, recycling and recycled content targets become more widespread, and the financial implications of using primary raw materials become more stringent. As it stands, there isn’t enough high-quality feedstock to meet this growing demand. Upgrades to the advanced mechanical recycling (AMR) process can solve this supply and demand challenge by:
- Closing the quality gap. With the latest technology, and the addition of new and enhanced steps to the traditional mechanical recycling process, AMR can produce high-quality recyclate from not only source separated waste, but from mixed waste streams as well.
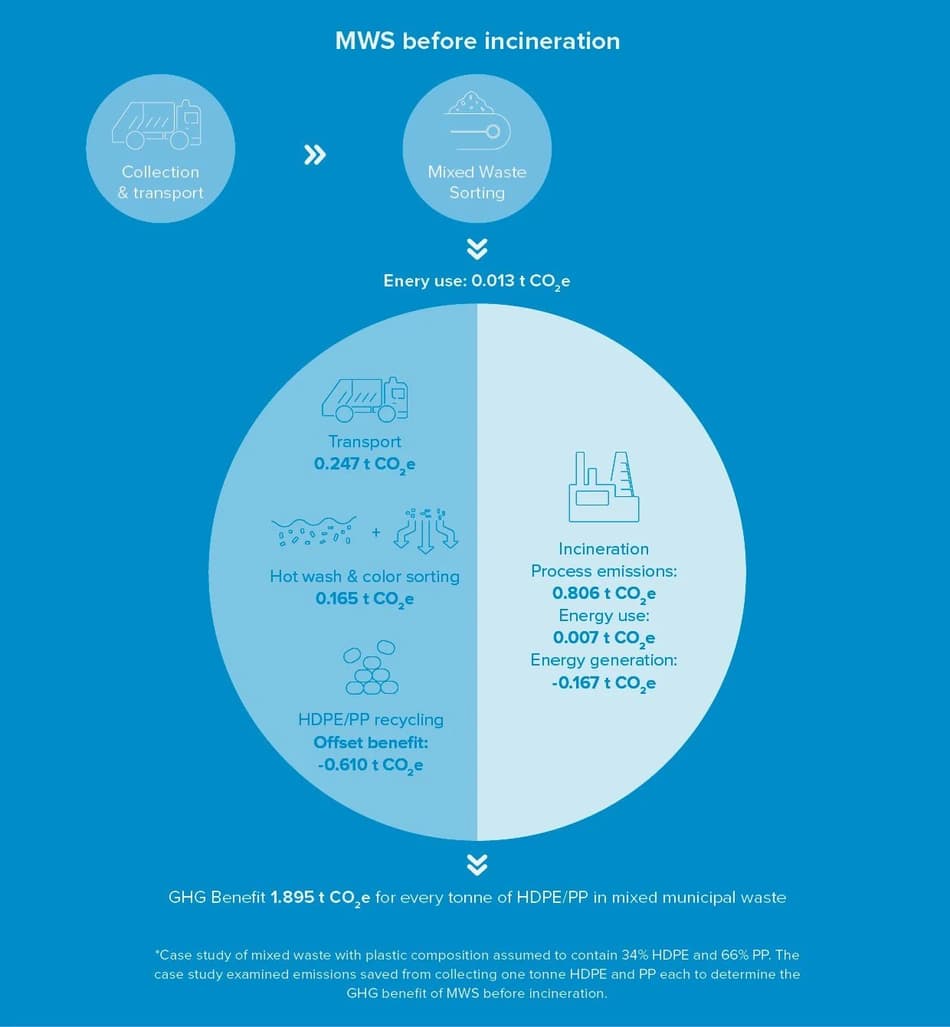
- Closing the quantity gap. Rescuing a large amount of waste that would otherwise end up in landfills or incinerators and processing it into virgin-like recyclate is imperative to producing sufficient amounts of recycled content. Mixed waste sorting (MWS) can achieve this.
When AMR is coupled with MWS, it is possible to fill the ever-growing demand for high-quality recyclates. To achieve true resource circularity, these solutions must be implemented at scale, therefore, investment in infrastructure is vital.

Closing the quality and quantity gaps
Today, only 2% of plastic packaging is recycled in closed-loop systems. By 2030, TOMRA aims to enable the collection of 40% of post-consumer plastic packaging, and the closed-loop recycling of 30% of all post-consumer plastic packaging. To achieve these ambitious commitments, the quality and quantity gaps across the value chain must be closed.
TOMRA's webcast: Advanced mechanical recycling: Enabling true circularity for plastics, now
Watch two industry experts discuss how we can close existing quality and quantity gaps along the plastics value chain by producing enough virgin-line recyclate from different material streams - including mixed waste streams - with advanced mechanical recycling.